[vc_toggle title=”WHAT IS ISO 9001:2015 – QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS?”]For some of the best understanding, we have added some links to external website.
ISO 9001 is defined as the international standard that specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Organizations use the standard to demonstrate the ability to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements. It is the most popular standard in the ISO 9000 series and the only standard in the series to which organizations can certify.
ISO 9001 was first published in 1987 by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), an international agency composed of the national standards bodies of more than 160 countries. The current version of ISO 9001 was released in September 2015.
- Who should use the 9001:2015 revision?
- What are the benefits of ISO 9001?
- ISO 9001 certification
- ISO 9001 resources
WHO SHOULD USE THE ISO 9001:2015 REVISION?
ISO 9001:2015 applies to any organization, regardless of size or industry. More than one million organizations from more than 160 countries have applied the ISO 9001 standard requirements to their quality management systems.
Organizations of all types and sizes find that using the ISO 9001 standard helps them:
- Organize processes
- Improve the efficiency of processes
- Continually improve
All organizations that use ISO 9001 are encouraged to transition to ISO 9001:2015 as soon as possible. This includes not only organizations that are certified to ISO 9001:2008, but also any organizations involved in training or certifying others.
As of September 14, 2018 organizations that are currently registered to ISO 9001:2008 should have transitioned to the 2015 standard.
Guidance on transitioning from ISO 9001:2008 to ISO 9001:2015 can be downloaded from the International Accreditation Forum (IAF).
Purchase ISO 9001:2015
Published hard copy
PDF e-standard

View the entire ISO Standards-Auditing Catalog
What topics does ISO 9001:2015 cover?
ISO 9001 is based on the plan-do-check-act methodology and provides a process-oriented approach to documenting and reviewing the structure, responsibilities, and procedures required to achieve effective quality management in an organization. Specific sections of the standard contain information on many topics, such as:
- Requirements for a QMS, including documented information, planning and determining process interactions
- Responsibilities of management
- Management of resources, including human resources and an organization’s work environment
- Product realization, including the steps from design to delivery
- Measurement, analysis, and improvement of the QMS through activities like internal audits and corrective and preventive action
Changes introduced in the 2015 ISO 9001 revision are intended to ensure that ISO 9001 continues to adapt to the changing environments in which organizations operate. Some of the key updates in ISO 9001:2015 include:
- The introduction of new terminology
- Restructuring some of the information
- An emphasis on risk-based thinking to enhance the application of the process approach
- Improved applicability for services
- Increased leadership requirements
The Seven Principles of ISO 9001:2015
How do I get started with ISO 9001:2015?
Whether you are beginning your ISO 9001 journey or transitioning to the 2015 revision, your first step is to purchase a copy of ISO 9001:2015.
As of September 14, 2018 organizations that are currently registered to ISO 9001:2008 should have transitioned to the 2015 standard.
Previous versions of ISO 9001
Originally published in 1987, ISO 9001 underwent revisions in 1994, 2000, and again in 2008. The latest revision was published in September 2015.
- ISO 9001:1994 included changes to improve the control of design and development clause, as well as provide other clarifications. The 1994 series also slightly modified the role of ISO 9002 and 9003.
- The ISO 9001:2008 revision sought to clarify issues raised during the application of ISO 9001:2000.
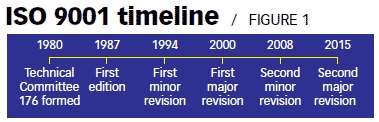
ISO 9001 Timeline
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF ISO 9001?
ISO 9001 helps organizations ensure their customers consistently receive high quality products and services, which in turn brings many benefits, including satisfied customers, management, and employees.
Because ISO 9001 specifies the requirements for an effective quality management system, organizations find that using the standard helps them:
- Organize a QMS
- Create satisfied customers, management, and employees
- Continually improve their processes
- Save costs
In Nevada, the Clark County School District used ISO 9001 to save $174 million over 10 years in actual expenditures and cost avoidance. More than 3,000 employees were trained to the standard, enabling three critical components of the system’s success: training, communication and respect, and efficiency.
ISO 9001 CERTIFICATION
ISO 9001 is the only standard in the ISO 9000 series to which organizations can certify. Achieving ISO 9001:2015 certification means that an organization has demonstrated the following:
- Follows the guidelines of the ISO 9001 standard
- Fulfills its own requirements
- Meets customer requirements and statutory and regulatory requirements
- Maintains documentation
Certification to the ISO 9001 standard can enhance an organization’s credibility by showing customers that its products and services meet expectations. In some instances or in some industries, certification is required or legally mandated. The certification process includes implementing the requirements of ISO 9001:2015 and then completing a successful registrar’s audit confirming the organization meets those requirements.
Organizations should consider the following as they begin preparing for an ISO 9001 quality management system certification:
- Registrar’s costs for ISO 9001 registration, surveillance, and recertification audits
- Current level of conformance with ISO 9001 requirements
- Amount of resources that the company will dedicate to this project for development and implementation
- Amount of support that will be required from a consultant and the associated costs
Read “What’s the cost?” for a checklist you can use to assess the costs of certifying to ISO 9001.
Note: ASQ does not issue ISO 9001 certification.
Courses in the ISO 9001 Standard
Training can provide an opportunity to review the ISO 9001:2015 standard and apply quality management principles in a practice environment.
Professionals responsible for developing, implementing, auditing, and managing an ISO quality management system or quality professionals interested in updating their documented ISO 9001-based QMS can take ISO 9000 training courses, which include courses focused on ISO 9001 and quality management systems. Additionally, organizations looking to improve employee performance and employees looking to continually improve will also find ISO 9000 training relevant.
- 16 Hour ISO 9001: 2015 Lead Auditor Training Exemplar Global Certified
- Documentation in ISO 9001: 2015
- Implementing and Auditing an ISO 9001: 2015 Quality Management System
- ISO 9001: 2015 Certified Internal Auditor (Quality Management System Training)
- ISO 9001: 2015 Certified Lead Auditor (Quality Management System Training)
- ISO 9001: 2015 Foundations
- ISO 9001: 2015 Requirements from A to Z
- ISO Lesson Guide: 9001 2015 Made Easy
- More ISO 9001 courses
ISO 9001 RESOURCES
You can also search articles, case studies, and publications for ISO 9001 resources.
ISO 9001:2015 Standard
The 2015 revision to ISO 9001, the international standard specifying requirements for quality management systems, is available for purchase in these formats:
- Published hard copy
- PDF e-standard for immediate download (please note that e-standards cannot be printed)
- Site license for posting an electronic version to your Local Area Network or Intranet
- Request for Interpretation (RFI) for ISO 9001:2015
Example Quality Manual
Need to write a quality manual that conforms to ISO 9001:2015? Download an example quality manual and read about how to create one.
Books
- Cracking the Case of ISO 9001: 2015 for Manufacturing
- Cracking the Case of ISO 9001: 2015 for Service
- How to Audit ISO 9001:2015
- How to Establish a Document Control System for Compliance with ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485:2016, and FDA Requirements
- ISO 9001:2015 Explained
- The ISO 9001: 2105 Implementation Handbook
- ISO 9001:2015 Handbook for Small and Medium-Sized Businesses
- ISO 9001:2015 Internal Audits Made Easy
- The Magic of ISO 9001
- A Practical Field Guide For ISO 9001: 2015
Articles
- Auditing Strategy for ISO 9001:2015 (Journal for Quality and Participation) When standards and other frameworks are used as models for an organization’s processes, having a suitable audit strategy can ensure appropriate compliance and corrective action.
- The Influence Of Human Factors On ISO 9001:2015 Compliance (Journal for Quality and Participation) Understanding the importance of people is crucial to the success of any management system. The ISO 9001 model is no different.
- ISO 9001:2015 Transition Starts With Top Management (PDF) Why leadership needs to be directly involved in the transition to ISO 9001:2015.
- A New Look (Quality Progress) 15 things you need to know now about the 2015 revision of ISO 9001.
Case Studies
- (E)Quality for All: You, Your Job, and ISO 9001 (PDF) ISO 9001 certification affects everything from how your customers perceive you, to how effective your processes are, to your organization’s ability/qualification to bid on major projects.
- Imaging Core Lab Takes Quality Beyond Regulatory Requirements with ISO 9001 (PDF) Though MMI’s ISO 9001 certification is recent, it is already seeing improvements to the timeliness of deliverables to clinical trial sponsors, an increase in quality awareness from the implementation, and positive feedback from sponsors.
Videos
- ISO 9001:2015 Overview As you get ready to implement or transition to ISO 9001:2015, it’s helpful to get a high-level overview of the standard before jumping in.
- ISO 9001:2015 – 15 Things You Must Know Now In this video interview, Paul Palmes discusses the ISO 9001 revision and key points organizations must consider as the draft international standard progresses through the development process.
- Team Builds ISO 9001 QMS on Wiki Learn how Geometrica, a dome manufacturer based in Texas and Mexico, involved its entire organization in documenting its quality management system for ISO 9001 certification using a Wiki.
- More ISO 9001 videos
Webcasts
- Improving Your QMS While Certifying to ISO 9001 Author Milt Dentch shares how organizations can go beyond ISO 9001:2015 compliance to substantially improve their quality management systems and the bottom line.
- Guidance on Conforming to ISO 9001:2015 Author Milton Dentch provides guidance on conforming to ISO 9001:2015.
- Lean ISO 9001 ISO 9001 expert Mike Micklewright walks through how and why documentation systems get out of control, what’s wrong with an overly lengthy documentation system, and how to get it back in control and make it more user friendly with the 5S lean tool.
- More ISO 9001 webcasts
[/vc_toggle][vc_toggle title=”WHAT IS ISO 14001:2015 – ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS?”]For some of the best understanding, we have added some links to external website.
- ISO 14001 is the international standard that specifies requirements for an effective environmental management system (EMS). It provides a framework that an organization can follow, rather than establishing environmental performance requirements.Part of the ISO 14000 family of standards on environmental management, ISO 14001 is a voluntary standard that organizations can certify to. Integrating it with other management systems standards, most commonly ISO 9001, can further assist in accomplishing organizational goals.The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) defines an environmental management system as “part of the management system used to manage environmental aspects, fulfill compliance obligations, and address risks and opportunities.” The framework in the ISO 14001 standard can be used within a plan-do-check-act (PDCA) approach to continuous improvement.
- Who should use the 14001:2015 revision?
- What are the benefits of ISO 14001?
- ISO 14001 certification
- ISO 14000 family of standards
- ISO 14001 resources
WHO SHOULD USE THE ISO 14001:2015 REVISION?
ISO 14001:2015 should be used by any organization that wishes to set up, improve, or maintain an environmental management system to conform with its established environmental policy and requirements. The requirements of the standard can be incorporated into any environmental management system, the extent to which is determined by several factors including the organization’s industry, environmental policy, products and service offerings, and location.
ISO 14001:2015 is relevant to all organizations, regardless of size, location, sector, or industry.
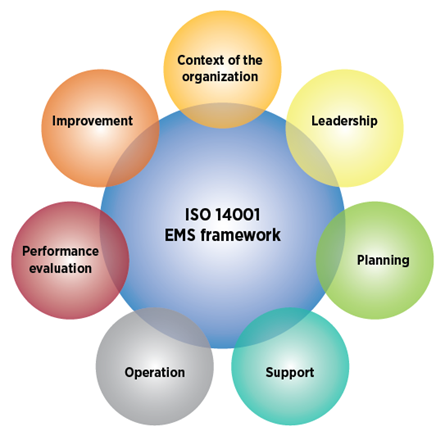
What topics does ISO 14001:2015 cover?
At the highest level, ISO 14001:2015 covers the following topics with regard to environmental management systems:
- Context of the organization
- Leadership
- Planning
- Support
- Operation
- Performance evaluation
- Improvement
ISO 14001 Environmental Management Systems (EMS) Framework

14001:2004 vs. 14001:2015
The 2015 revision of ISO 14001 introduces a number of changes from previous versions. A review of 20 years of research on this standard is available for ASQ member.
As part of the effort to structure all ISO standards in the same way, the ISO 14001:2015 revisions include incorporating a required high-level structure, using mandatory definitions, and incorporating common standards requirements and clauses.
10 major areas of impact of the 2015 revision:
- Expansion in EMS coverage and scope
- Required interactions with external parties
- New requirements for leadership engagement
- Expanded legal compliance requirements
- Need for risk-based planning and controls
- New documentation requirements
- Expanded operational control requirements
- Changes in competence and awareness requirements
- Impacts on the internal audit program
- Increased certification costs
Integrating ISO 9001 and ISO 14001
Integrating management systems standards can increase focus while reducing the potential for confusion. Elements of ISO 9001 can be enhanced with corresponding components of ISO 14001.
Responsibilities for the combined standards might include:
- Drafting a policy statement and quantifiable objectives
- Setting up organizational charts and job descriptions
- Providing adequate resources
- Managing documentation for both standards in a single document control system
- Appointing a management representative as well as coordinators for the quality and environmental managements systems
When adding ISO 14001 components to those of ISO 9001, planning must be expanded to deal with environmental impacts, and the inspection and test systems modified to cover environmental conformance. The organization must meet the environmental expectations of customers and the government, and it must incorporate environmental management elements into internal audit programs and training sessions.
ISO 14001 can be integrated with standards besides ISO 9001 in order to provide synergy with other systems, such as OHSAS 18001 and ISO 13485.
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF ISO 14001:2015?
Using ISO 14001:2015 has many benefits for organizations with environmental management systems. Organizations and companies find that using the standard helps them:
- Improve resource efficiency
- Reduce waste
- Drive down costs
- Provide assurance that environmental impact is being measured
- Gain competitive advantage in supply chain design
- Increase new business opportunities
- Meet legal obligations
- Increase stakeholder and customer trust
- Improve overall environmental impact
- Manage environmental obligations with consistency
ISO 14001 CERTIFICATION
Organizations that have already achieved ISO 14001 certification are encouraged to transition to the 2015 version. Organizations will have a three-year transition period to update their environmental management systems to the new standard.
To get started with ISO 14001:2015:
- Review existing quality management system requirements (ISO 9001:2015)
- Purchase ISO 14001:2015
- Get ISO 14001 training
- Certify to ISO 14001
ISO 14000 FAMILY OF STANDARDS
ISO 14001 is the most popular standard of the ISO 14000 family, which also includes standards such as the following:
- ISO 14004:2016 – Environmental Management Systems – General Guidelines On Implementation
- ISO 14006:2011 – Environmental Management Systems – Guidelines For Incorporating Ecodesign
- ISO 14015:2001 – Environmental Management – Environmental Assessment Of Sites And Organizations (EASO)
- ISO 14020:2000 – Environmental Labels And Declarations – General Principles
- ANSI/ISO 14025:2006 – Environmental Labels And Declarations – Type III Environmental Declarations – Principles And Procedures
- ISO 14031:2013 – Environmental Management – Environmental Performance Evaluation – Guidelines
- ISO 14040:2006 – Environmental Management – Life Cycle Assessment – Principles And Framework
- ASQ/ANSI/ISO 14044:2006 – Environmental Management – Life Cycle Assessment – Requirements And Guidelines
- ISO/TR 14047:2012 – Environmental Management – Life Cycle Assessment – Illustrative Examples On How To Apply ISO 14044 To Impact Assessment Situations
- ISO/TR 14049:2012 – Environmental Management – Life Cycle Assessment – Illustrative Examples On How To Apply ISO 14044 To Goal And Scope Definition And Inventory Analysis
- ISO 14050:2009 – Environmental Management – Vocabulary
- ISO 14063:2006 – Environmental Management – Environmental Communication – Guidelines And Examples
- ISO 14064-1:2018 – Greenhouse Gases – Part 1: Specification With Guidance At The Organization Level For Quantification And Reporting Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Removals
- ISO 14064-2:2019 – Greenhouse Gases – Part 2: Specification With Guidance At The Project Level For Quantification, Monitoring And Reporting Of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions Or Removal Enhancements
- ISO 14064-3:2019 – Greenhouse Gases – Part 3: Specification With Guidance For The Verification And Validation Of Greenhouse Gas Statements
- ISO 14067:2018 – Greenhouse Gases – Carbon Footprint Of Products – Requirements And Guidelines For Quantification
- ISO/TR 14069:2013 – Greenhouse Gases – Quantification And Reporting Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions For Organizations
- ISO/TS 14071:2014 – Environmental Management – Life Cycle Assessment – Critical Review Processes And Reviewer Competencies: Additional Requirements And Guidelines To ISO 14044:2006
- ISO/TS 14072:2014 – Environmental Management – Life Cycle Assessment – Requirements And Guidelines For Organizational Life Cycle Assessment
- ISO 19011:2018 – Guidelines For Auditing Management Systems
ISO 14001 RESOURCES
You can also search articles, case studies, and publications for ISO 14001 resources.
Books
The ISO 14001:2015 Implementation Handbook
A Practical Field Guide For ISO 14001:2015
Articles and Case Studies
ISO 14001 Standard: Literature Review And Theory-Based Research Agenda (Quality Management Journal) Environmental sustainability has gained momentum in the business world and academia. After about 20 years of research in this field, this paper presents a holistic literature review specifically focused on ISO 14001, which is widely considered the most important environmental certification.
Stewardship And Sustainability: Serigraph’s Journey To ISO 14001 (Journal for Quality and Participation) Leaders of Serigraph understand that sustainability and social responsibility require the simultaneous promotion of equitable economic growth, environmental protection, and social well-being. Serigraph uses ISO 14001, Six Sigma, and lean as its templates for environmental and sustainability improvement.
A Framework For The Development Of An Environmental Management System: A Case Study In A Thermal Power Plant (Quality Engineering) Questions regarding implementation of ISO 14001 prompted NP Power, the electric power company of New Brunswick, Canada, to develop a framework to assess its compliance to the standards.
[/vc_toggle][vc_toggle title=”WHAT IS CE MARKING? UNDERSTANDING TO EN STANDARDS”]The Conformité Européene (CE) Mark is defined as the European Union’s (EU) mandatory conformity marking for regulating the goods sold within the European Economic Area (EEA) since 1985. The CE marking represents a manufacturer’s declaration that products comply with the EU’s New Approach Directives. These directives not only apply to products within the EU but also for products that are manufactured in or designed to be sold in the EEA. This makes the CE marking recognizable worldwide even to those unfamiliar with the EEA.
HOW DOES THE CE MARK WORK?
A CE Mark is a symbol that must be affixed to many products before they can be sold on the European market. The mark indicates that a product:
- Fulfills the requirements of relevant European product directives
- Meets all the requirements of the relevant recognized European harmonized performance and safety standards
- Is fit for its purpose and will not endanger lives or property
Conformité Européene Mark (CE Mark)

The presence of CE marking further indicates that appropriate technical documentation supporting the use of the mark is available and can be provided by the manufacturer, importer, or person responsible for placing the product on the EU market upon request.
CE MARK CERTIFICATION VS. SELF-DECLARATION
CE marking does not provide any specific information to the consumer. It is not a quality assurance declaration, it does not show evidence of third-party testing, and it should not be confused with any independent certification mark of the type issued by international or European notified test bodies.
Certain directives include an option for the responsible organization to provide a declaration of conformity stating that a product fulfills the requirements of the applicable directives. However, if challenged, the appropriate evidence must be supplied to support the self-declaration claim. Other directives, particularly those pertaining to products affecting health and/or safety, such as pressure vessels, will require a specific certificate from a notified body.
MEETING EU CE MARK REQUIREMENTS AND CONFORMING TO DIRECTIVES
Affixing a CE Mark to a product is considered a means to certify for authorities within the EU member states that the product meets all appropriate EU requirements.
There is an EU requirement that products not in conformity with the provisions of the directives are not allowed to circulate in the territories of the member states; appropriate action should be taken to remove these products from sale and use within the specific state. One example is the recent import of toys from China to the UK which, when examined, were found to contain a high level of poisonous toxins that endanger life.
The importer and/or manufacturer must take steps to comply with safety provisions, produce the appropriate records, and decide on the necessary procedures to maintain production in conformity with directives. The CE Mark must be affixed to demonstrate conformity with the provisions of the directives.
Specific directives have comprehensive safety objectives, but they leave the manufacturer to make decisions on how these may be achieved.
Where more than one CE Mark directive pertains to a product and a transitional period allows the manufacturer a choice of which to apply, the marking indicates conformity only with those directives applied by the manufacturer. In this case the directives that have been applied must be identified in the documents or notices accompanying the product. Where the manufacturer does not list those directives that have been applied, the authorities will assume that a declaration of conformity is available for all applicable directives.
THE BOTTOM LINE IN DEMONSTRATING CE MARK CONFORMITY
Any organization manufacturing or selling products in the EU should be aware of its obligations when it comes to demonstrating conformity to requirements and directives:
- The CE Mark must be affixed to demonstrate conformity with the provisions of the directives.
- In the event of a challenge, a report from a notified body may be submitted showing conformity of the equipment. This allows the manufacturer working with a notified body to show conformity with the safety objectives.
CE MARK REFERENCES AND ARTICLES
- See the entry on CE marking on the European Commission’s website.
- See the European Commission’s CE Marking website.
Concerning gloves PPE users (Directive 89/656 dated 30.11.1989 and the associated texts).
Obligations are fixed in the PPE users” Directive 89/656 dated 30.11.1989 and the associated texts.
Employers of people using PPE must insure that they analyse and assess, in collaboration with the various internal committees, the weaknesses of the protection systems.
In accordance with the definition above, they select personal protective equipment with the appropriated level of protection necessary in view of the potential danger and risk likely to be incurred.
They provide personal protective equipment free of charge and conforming to the legal requirements, i.e.:
- CE marked ;
- with user information attached to each pair of glove;
- with a declaration of conformity given to the user during the purchase phase.
CE TYPE-EXAMINATION
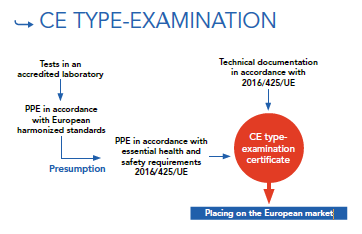
Concerning Gloves PPE manufacturers (“PPE design” Regulation 2016/425/UE).
CE marking is based on the following texts: “PPE design” Regulation 2016/425/UE
Manufacturers must place PPE gloves on the market that comply with the essential requirements of European Regulation 2016/425/EU.
For this purpose, they are required to:
A – Characterize the product / Define the risks
PPE certification Rules – PPE Gloves
| Certification rules | Category I | Category II | Category III |
| CLASSIFICATION | Minor risks | Other risks | Lethal or irreversible risks |
| EXAMPLES | Gardening glove | Glove for mechanical risks | Glove for chemical risks |
| OBLIGATIONS OF THE MANUFACTURER |
|
Category I
+
|
Category II
+
|
B – Choose the PPE gloves standard
ANSI/ISEA 105 |
Hand Protection Classification |
EN ISO 374-1 |
Protective gloves against dangerous chemicals and microorganisms – Part 1: Terminology and performance requirements for chemical risks |
EN ISO 374-5 |
Protective gloves against dangerous chemicals and microorganisms – Part 5: Terminology and performance requirements for micro-organisms risks |
EN 388 |
Protective gloves against mechanical risks |
EN 407 |
Protective gloves against thermal risks (heat and/or fire) |
EN 421 |
Protective gloves against ionizing radiation and radioactive contamination |
EN 511 |
Protective gloves against cold |
EN 659 |
Protective gloves for firefighters |
EN 1082 |
(part 1 to 3) Protective clothing – Gloves and arm guards protecting against cuts and stabs by hand knives |
EN ISO 10819 |
Mechanical vibration and shock – Hand-arm vibration – Measurement and evaluation of the vibration transmissibility of gloves at the palm of the hand |
EN ISO 11393-4 |
Protective clothing for users of hand-held chain-saws – Part 4: Test methods and performance requirements for protective gloves |
EN 12477 |
Protective gloves for welders |
EN 13594 |
Protective gloves for motorcycle riders – Requirements and test methods |
EN ISO 13997 |
Protective clothing – Mechanical properties – Determination of resistance to cutting by sharp objects |
EN 14328 |
Protective clothing – Gloves and armguards protecting against cuts by powered knives – Requirements and test methods |
EN 16027 |
Protective clothing – Gloves with protective effect for association football goal keepers |
EN 16350 |
Protective gloves – Electrostatic properties |
EN 16523 |
(parties 1 et 2) Determination of material resistance to permeation by chemicals |
EN 16778 |
Protective gloves – The determination of Dimethylformamide in gloves |
EN 18889 |
Protective gloves for pesticide operators and re-entry workers – Performance requirements |
EN ISO 21420 |
Protective gloves – General requirements and test methods |
D- Safety gloves marking system
All gloves marked CE guarantee a high level of protective, comfort and durability established on the basis of the following marking standards :
- Gloves must comply with the requirements of the European Regulation. The compliance is established by the implementation of harmonized European standards applicable in all the countries of the European Community.
- In addition to the CE marking, the international standards enforce a secondary indication allowing the identification of the protection afforded by the gloves.
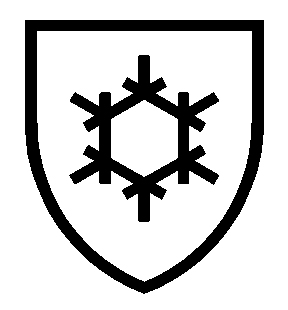
| MECHANICAL RISKS EN 388 – WXYZα (P) | COLD RISKS EN511 – XYZ | CHEMICAL RISKS EN ISO 374-1 |
 |  |  |
|
| Permeation resistance + letters corresponding to the tested chemical
|
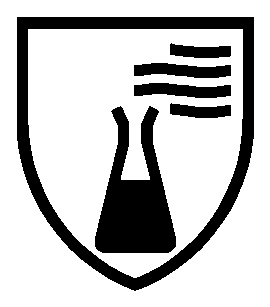
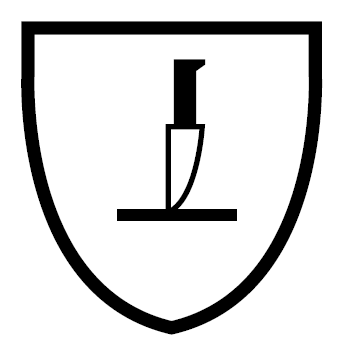
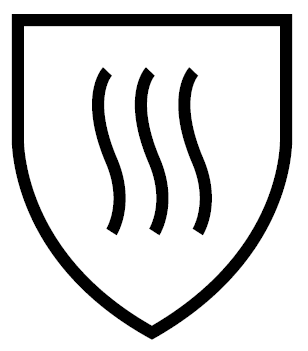
| IMPACT CUT EN 1082 | MICRO-ORGANISM HAZARDS EN ISO 374-5 | THERMAL RISKS EN 407 – UVWXYZ |
 |  |   |
| ||
| RADIOACTIVE CONTAMINATION EN 421 | HEAT AND FIRE HAZARDS FOR FIREFIGHTERS – EN 659 | |
 |  | |
| HAND HELD CHAINSAWS EN ISO 11393-4 | MOTORCYCLE RIDERS EN 13594 | |
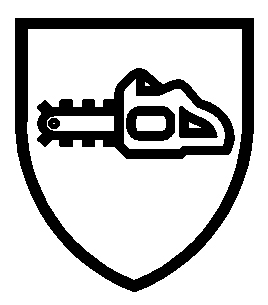 |  | |
INFORMATION | PESTICIDES RISKS EN ISO 18889 | |
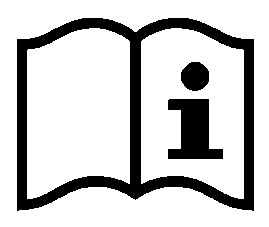 | 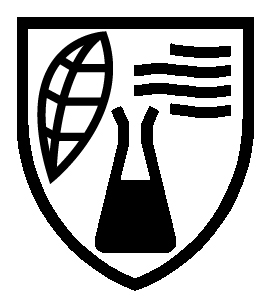 |
PPE Glove design
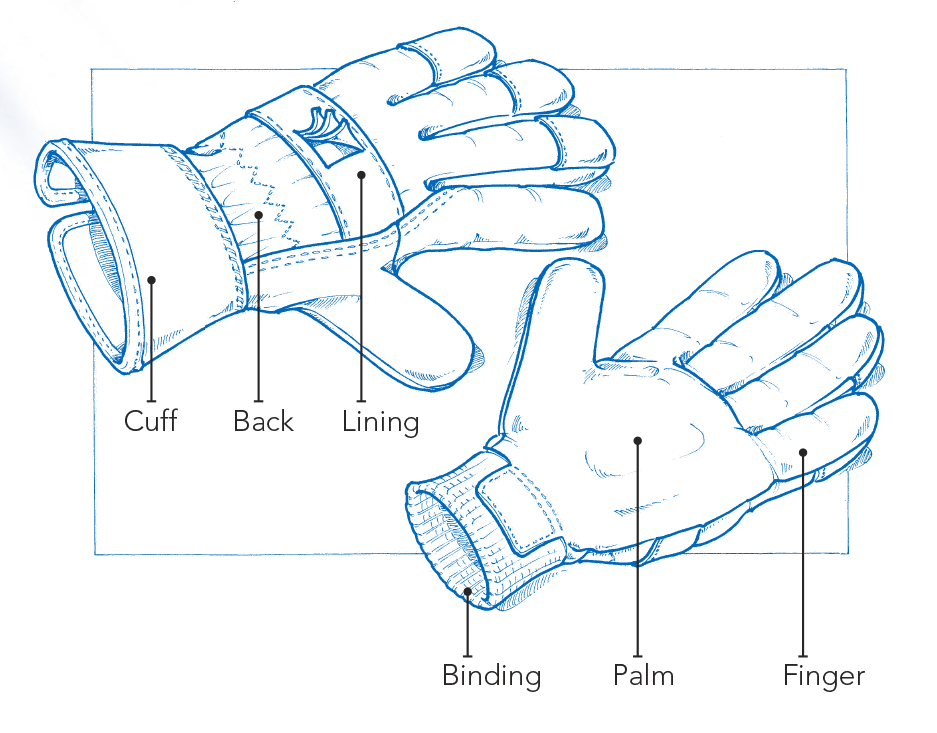
[/vc_toggle]